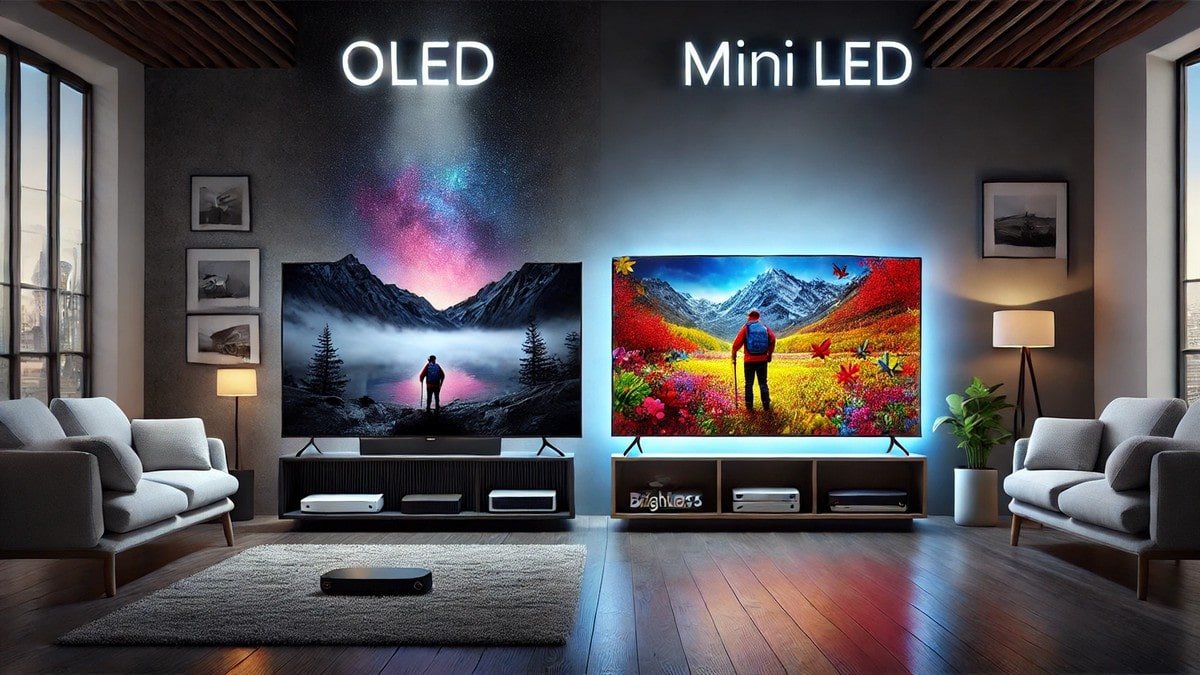
In the world of display technology, CES 2025 highlighted a heated debate between MiniLED vs OLED. Both technologies promise outstanding visual experiences, but their advantages, limitations, and ideal applications differ significantly. As a user, whether you are a business manager, a home theater enthusiast, or a tech-savvy consumer, understanding these differences is essential for making informed purchasing and installation decisions. This article provides a complete guide to MiniLED and OLED displays, their technical specifications, practical applications, maintenance tips, and trends showcased at CES 2025.
What Is MiniLED Technology?
MiniLED is an advanced backlighting solution for LCD panels. It utilizes thousands of tiny LEDs organized into numerous controllable zones, offering precise local dimming, higher brightness, and better contrast than traditional LED-backlit LCDs.
For example, in offices, bright spaces require displays that maintain visibility even under direct sunlight. MiniLED excels in these conditions. Users who have dealt with extreme temperatures can relate to Protecting Outdoor LED screen from Extreme Heat, as proper thermal management is crucial for performance and longevity.
MiniLED displays also allow for thin and modular designs, making them adaptable to various environments, from corporate lobbies to retail showrooms.
 Understanding OLED Technology
Understanding OLED Technology
OLED, or Organic Light-Emitting Diode, uses self-emitting pixels, meaning each pixel produces its own light. This results in true blacks, infinite contrast ratios, and vibrant color reproduction. However, OLEDs are limited in peak brightness compared to MiniLEDs and can experience burn-in over prolonged static content display.
For home theaters and rooms with controlled lighting, OLED’s deep blacks and wide viewing angles offer unmatched cinematic experiences. Choosing between MiniLED vs OLED depends largely on the ambient environment, content type, and usage frequency.
Key Technical Specifications to Consider
When selecting a display, several specifications impact performance:
-
Brightness: MiniLEDs can reach thousands of nits, ideal for bright environments. OLEDs peak at 600–700 nits but excel in dark scenes.
-
Contrast Ratio: OLED provides infinite contrast with perfect blacks, while MiniLED achieves high contrast using local dimming zones.
-
Color Accuracy: MiniLED leverages quantum dot enhancements to maintain accurate colors even at high brightness, while OLED produces naturally rich colors.
-
Viewing Angle: OLED maintains consistent colors and contrast across angles; MiniLED’s performance depends on the LCD panel technology.
-
Refresh Rate: Both support 60Hz–120Hz or higher, important for gaming, video, or office dashboards.
-
Durability: MiniLED avoids burn-in issues, while OLED may require cautious content rotation.
Understanding these details helps users, especially when considering Office Digital Signage Specs, to match display capabilities with environment needs.
Applications of MiniLED and OLED
1. Corporate Offices
-
MiniLED: High-brightness, large-scale video walls for open office spaces or lobbies. Supports presentations, dashboards, and collaboration tools.
-
OLED: Ideal for executive offices, conference rooms, or smaller environments requiring cinematic-quality visuals.
2. Retail and Restaurants
-
MiniLED displays maintain visibility under sunlight and can be used for menus or promotional signage. Regular checks inspired by Outdoor LED Screen Maintenance ensure long-term reliability.
-
OLED provides immersive product showcases in indoor, dimly-lit stores or experiential marketing zones.
3. Home Theaters and Entertainment
-
OLED dominates in dark rooms, offering the ultimate cinema experience.
-
MiniLED can achieve HDR brightness in bright living rooms, providing flexibility for multi-use spaces.
4. Specialized Uses
-
Gaming monitors benefit from high refresh rates of both technologies.
-
Large event venues can leverage MiniLED modularity and brightness for stage displays.
Advantages of MiniLED
-
High Brightness and Visibility: Suitable for sunlit environments.
-
Dynamic Local Dimming: Improves contrast without the burn-in risk of OLED.
-
Modularity: Screens can be customized for size and shape.
-
Energy Efficiency: Consumes less power than OLED at peak brightness.
The technology also overlaps with Micro LED Displays research, showing potential for future hybrid displays combining the best of both worlds.
Advantages of OLED
-
Perfect Blacks and Infinite Contrast: Unmatched cinematic quality.
-
Wide Viewing Angles: Colors and contrast remain consistent.
-
Thin Form Factor: No backlight, allowing ultra-slim designs.
-
Vivid Color Reproduction: Ideal for creative content and entertainment.
These advantages make OLED unbeatable in environments with controlled lighting and for high-end home setups.
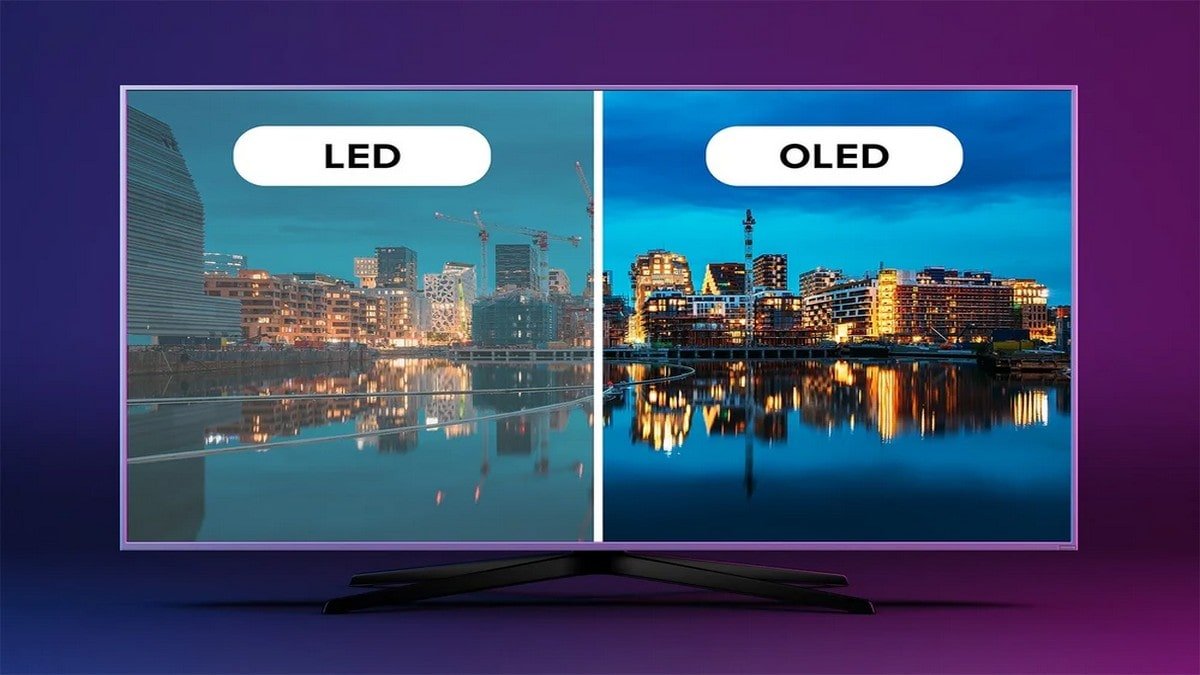 CES 2025 Trends
CES 2025 Trends
CES 2025 showcased rapid adoption of MiniLED technology across consumer and professional markets. Brands like LG, Samsung, and TCL demonstrated:
-
MiniLED TVs with Quantum Dots: Enhanced color and contrast.
-
High Brightness Displays: Suitable for daylight viewing.
-
Thin, Modular Screens: Adaptable for office lobbies or conference rooms.
Consumer awareness is growing about MiniLED vs OLED, and many users now base their purchasing decisions on environment suitability, usage type, and content needs.
Practical Tips for Choosing the Right Display
Evaluate Your Environment
-
Bright offices, retail spaces, and sunlit rooms → MiniLED.
-
Dark theaters, home cinemas → OLED.
Consider Content Type
-
HDR-heavy content and interactive signage → MiniLED.
-
Cinematic films, graphic design, photography → OLED.
Longevity and Maintenance
-
Rotate static content on OLED to avoid burn-in.
-
Apply MiniLED maintenance techniques similar to Outdoor LED Screen Maintenance to ensure performance.
Integration
-
MiniLED modularity allows combination with Office Digital Signage Specs for corporate dashboards.
-
OLED suits creative studio environments where image fidelity is crucial.
Challenges and Considerations
-
MiniLED: Higher cost, manufacturing complexity, potential blooming in local dimming zones.
-
OLED: Burn-in risk, lower peak brightness, higher cost in large formats.
-
Content Optimization: Both technologies require high-quality content to showcase full capabilities.
For commercial applications, intelligent solutions like AI-Powered Outdoor Screens suggest that automated brightness and adaptive content could further enhance MiniLED or OLED deployment.
Future Outlook
MiniLED vs OLED is not just a trend but a roadmap for the future of displays. Expected developments include:
-
Hybrid Technologies: Combining self-emissive pixels with MiniLED backlights.
-
Increased Adoption in Offices and Retail: Modular, bright, and versatile displays.
-
Consumer Electronics Expansion: TVs, monitors, laptops, and wearables.
-
Smart Integration: IoT, AI, and automated content delivery.
Understanding these trends ensures users make informed long-term investments and stay ahead in adopting advanced display technology.
Conclusion
MiniLED vs OLED represents a pivotal decision point in display technology. MiniLED excels in brightness, scalability, and durability, while OLED offers unmatched contrast, color accuracy, and cinematic experience. CES 2025 trends highlight MiniLED’s growing presence in professional and bright environments, but OLED remains the choice for high-end home and creative use. By considering environmental conditions, content type, longevity, and maintenance, users can confidently select the right display technology for their needs.




